=Python中的变量和引用=
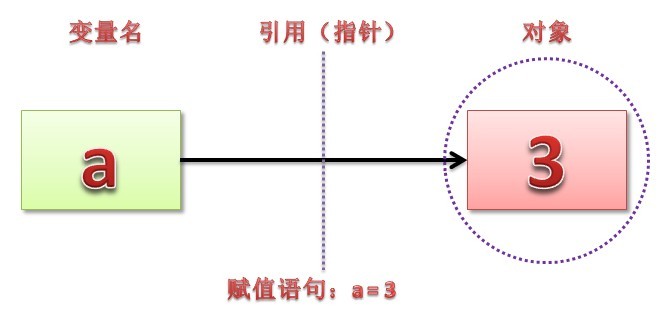
在 Python 中赋值语句总是建立对象的引用值,而不是复制对象。因此,Python 变量更像是指针,而不是数据存储区域。
在Python中,对象分为两种:可变对象和不可变对象,不可变对象包括int,float,long,str,tuple等,可变对象包括list,set,dict等。需要注意的是:这里说的不可变指的是值的不可变。对于不可变类型的变量,如果要更改变量,则会创建一个新值,把变量绑定到新值上,而旧值如果没有被引用就等待垃圾回收。另外,不可变的类型可以计算hash值,作为字典的key。可变类型数据对对象操作的时候,不需要再在其他地方申请内存,只需要在此对象后面连续申请(+/-)即可,也就是它的内存地址会保持不变,但区域会变长或者变短。
In [1]: a = 'ixyzero.com' In [2]: id(a) Out[2]: 53442592 In [3]: a = 'aol.com' In [4]: id(a) Out[4]: 53443904 # 重新赋值之后,变量a的内存地址已经变了 # 'ixyzero.com'是str类型,不可变,所以赋值操作知识重新创建了str对象'aol.com',然后将变量a指向了它 In [5]: aList = [1, 2, 3] In [6]: id(aList) Out[6]: 53941992 In [7]: aList.append(4) In [8]: id(aList) Out[8]: 53941992 # list重新赋值之后,变量 aList 的内存地址并未改变 # [1, 2, 3]是可变的,append操作只是改变了其value,变量 aList 指向没有变
参考链接:
- http://xianglong.me/article/python-variable-quote-copy-and-scope/
- http://my.oschina.net/leejun2005/blog/145911
- http://blog.upsuper.org/python-variable-type-and-reference.html
Python中函数参数的传递方式,值传递 or 引用传递?
简要的说:都不是(和传统的C/C++中的值传递、引用传递都不一样),是”call-by-object”。
搜索关键字:
python How are arguments passed
参考链接:
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/986006/how-do-i-pass-a-variable-by-reference
- http://robertheaton.com/2014/02/09/pythons-pass-by-object-reference-as-explained-by-philip-k-dick/
- https://www.jeffknupp.com/blog/2012/11/13/is-python-callbyvalue-or-callbyreference-neither/
Python中变量的作用域
参考解答:
变量分为三个作用域进行查找:首先是本地(Local),然后是函数内(如果有的话)(Enclosing),之后是全局(Global),最后是内置(Built-in)。在默认情况下,变量名赋值会创建或者改变本地变量。全局声明将会给映射到模块文件内部的作用域的变量名赋值。Python 的变量名解析机制也称为 LEGB 法则,具体如下:
当在函数中使用未确定的变量名时,Python搜索4个作用域:本地作用域(L),之后是上一层嵌套结构中 def 或 lambda 的本地作用域(E),之后是全局作用域(G),最后是内置作用域(B)。按这个查找原则,在第一处找到的地方停止。如果没有找到,Python 会报错。
参考链接:
- https://blog.mozilla.org/webdev/2011/01/31/python-scoping-understanding-legb/
- https://docs.python.org/2/faq/programming.html#why-am-i-getting-an-unboundlocalerror-when-the-variable-has-a-value
- http://www.toptal.com/python/top-10-mistakes-that-python-programmers-make
- http://blog.jobbole.com/68256/
=浅拷贝&深拷贝=
搜索关键字:
- python list copy a[:]
- python list copy list slice
参考链接:
- http://xianglong.me/article/python-variable-quote-copy-and-scope/
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/184643/what-is-the-best-way-to-copy-a-list
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2612802/how-to-clone-or-copy-a-list-in-python
- http://my.oschina.net/leejun2005/blog/145911
参考解答:
""" import copy a = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] b = a c = a[:] # slicing (shallow copy) d = copy.copy(a) # (shallow copy) e = copy.deepcopy(a) print id(a), id(b), id(c), id(d), id(e) b is a c is a d is a e is a a.append(15) a[1][2] = 10 print a print b print c print d print e """ In [24]: print id(a), id(b), id(c), id(d), id(e) 139922530241208 139922530241208 139922546974448 139922529937024 139922546974376 In [25]: b is a Out[25]: True In [26]: c is a Out[26]: False In [27]: d is a Out[27]: False In [28]: e is a Out[28]: False In [29]: a.append(15) In [30]: a Out[30]: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], 15] In [31]: b Out[31]: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], 15] In [32]: c Out[32]: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] In [33]: d Out[33]: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] In [34]: e Out[34]: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] In [35]: a[1][2] = 111 In [36]: a Out[36]: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 111], 15] In [37]: b Out[37]: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 111], 15] In [38]: c Out[38]: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 111]] In [39]: d Out[39]: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 111]] In [40]: e Out[40]: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
=EOF=
《“Python中的变量/引用/拷贝”》 有 1 条评论
Python 字典(Dictionary) copy()方法
https://www.runoob.com/python/att-dictionary-copy.html
Python 直接赋值、浅拷贝和深度拷贝解析
https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/python-understanding-dict-copy-shallow-or-deep.html